
Our Location
Contact Info
- 1 Rongmuang Rd. Rongmuang Pathumwan Bangkok 10330
- webmaster.srt@railway.co.th
- +66 1690
Passenger Operation
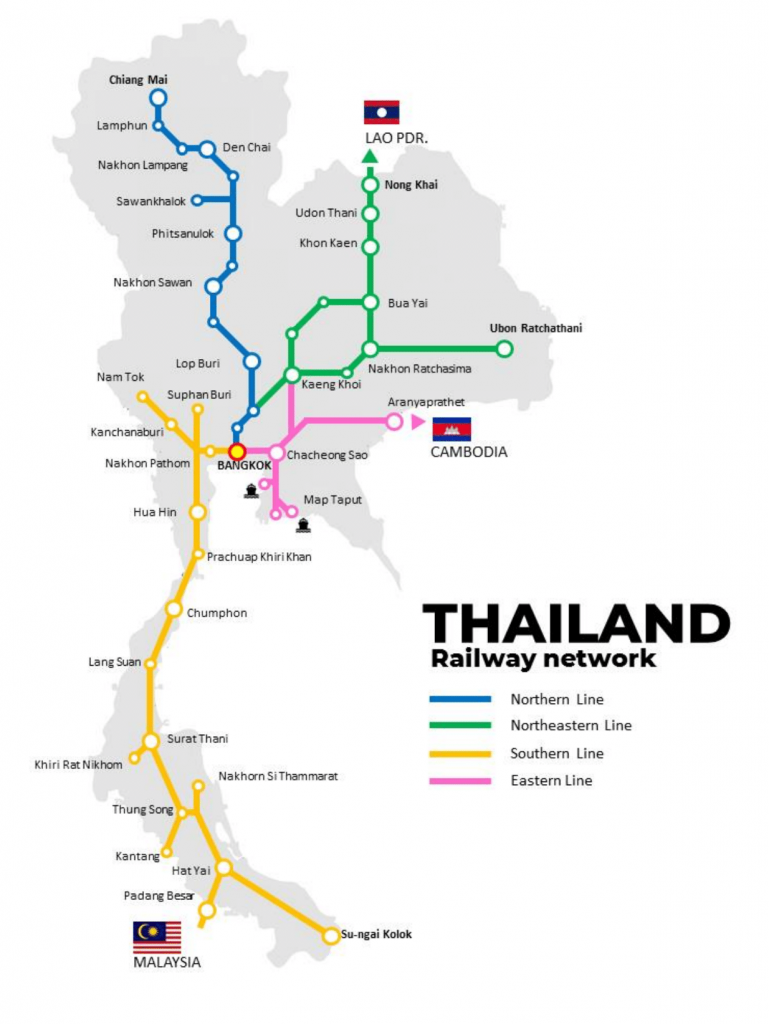
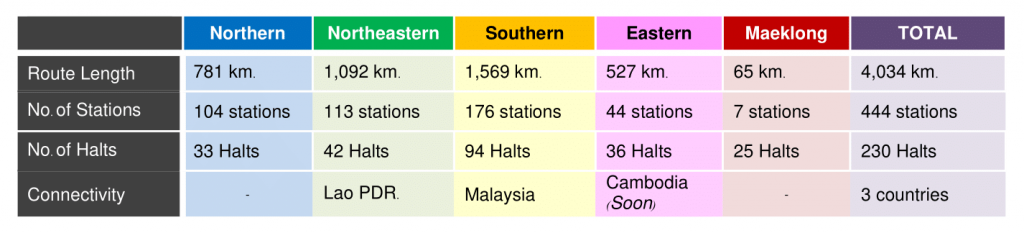
Presently, SRT operates four main lines radiating from Bangkok: the Northern Line that terminates at Chiang Mai; the Northeastern Line with two main lines running to Nong Khai and to Ubon Ratchathani; the East Line to Aranyaprathet connecting to Cambodian border; the Southern Line to Padang Besar, interchanging to Malaysian Railway; and Su-ngai Kolok, close to the Malaysian border.
Fiscal
In fiscal year 2018, the performance of SRT carried 36.8 million passengers increasing 1.8% from fiscal year 2017. SRT provides the Special Train 997/998 from Bangkok – Ban Plu Taluang – Bangkok on Saturday and Sunday since 17 March 2018 to support tourism in Pattaya, Sattahip and Chonburi which the one of most popular destination to the east coast of Thailand.
Additionally, SRT has planned to purchase the 184 DMU and 273 passenger cars for commercial long distance train service and the 216 DMU for public service obligation (PSO).
Rail Network
Status of SRT Trains
SRT provides 263 trains per day which include 152 PSO trains and 84 commercial trains as below:
First class (1st class)
- Air-conditioned sleeper coach with 2 berths in a private room
Second class (2nd class)
- Type 1: Sleeper coach – Each coach, there are 32 – 40 berths in both air-conditioned and non-air-conditioned type.
- Type 2: Reclining seat – Each coach, there are 30 – 76 reclining seats in both air -conditioned and non-air-conditioned type.
Third class (3rd class)
- There are 74-76 seats in each non-air-conditioned coach.
Freight Operation
In fiscal year 2017, SRT transported 11.91 million tons of freight, generating approximately 1.74 million baht in revenue, which represented an increase amount 2.39% and increase revenue of 6% from previous fiscal year. The 12 CSR Ziyang Locomotives of TPIPL Company for cement haulage increased 34.02%.
SRT has planned to implement five projects of freight in 2018:
- Business partnership for products export
- Freight stations facilities development with private sector
- Increasing the domestic container train
- Increasing the container train in ICD Lad Krabang – Laem Chabang Port
- Logistic service system development with domestic partnership. In addition, including 100 Locomotives (Passenger & Freight) and 800 – 1,000 BCFs after the completion of double tracking project.
Service Planning
According to the infrastructure projects in various fields, SRT plans to service and operate when the said projects are mostly completed to increase the performance by making the rail transportation more convenient and meeting customers’ needs. Presently, SRT plans to procure the new locomotives, passenger train sets, DMUs and freight cars are as follows:-
- 50 Diesel-Electric Locomotives
- 20 Shunting Locomotives (for Red Line and Bangsue Grand Station)
- 50 Electric Locomotive for launching electrified train
- 216 DMUs for PSO services
- 184 DMUs for long distance services
- 273 Passenger cars for replace and new long distance train services
- 208 Passenger cars for replacement
- Passenger Trains and DMUs for new line (Chiang Khong and Nakhon Panom)
SRT prepares to reorganize the commuter train and ordinary train service when Bangsue Grand Station open, the commuter and ordinary train will relocate origin/destination station from Bangkok to Rangsit (north and northeastern line PSO trains) and Taling Chan (southern line PSO trains).
Moreover, SRT prepares to improve ticketing service. The Ticket and Reservation System Stage 2 (STAR-2) is presently used until 2020. SRT will reveal and launch a new ticketing and reservation system called D-Ticket in 2020.
When SRT ascertains customers’ needs, the new performance of D-Ticket will give passengers more convenient. Passengers can book a seat via every railway station, mobile application and website. They can also check their reservation by QR code. About present payments, passengers can pay by cash, credit card and debit card. In the future, SRT will provide a variety of payment methods such as Counter Service at convenience stores, post offices, banks and digital payment.
