Our Location
Contact Info
- 1 Rongmuang Rd. Rongmuang Pathumwan Bangkok 10330
- webmaster.srt@railway.co.th
- +66 1690
Introduction to State Railways of Thailand

" To be the best state rail operator in ASEAN in 2027 "
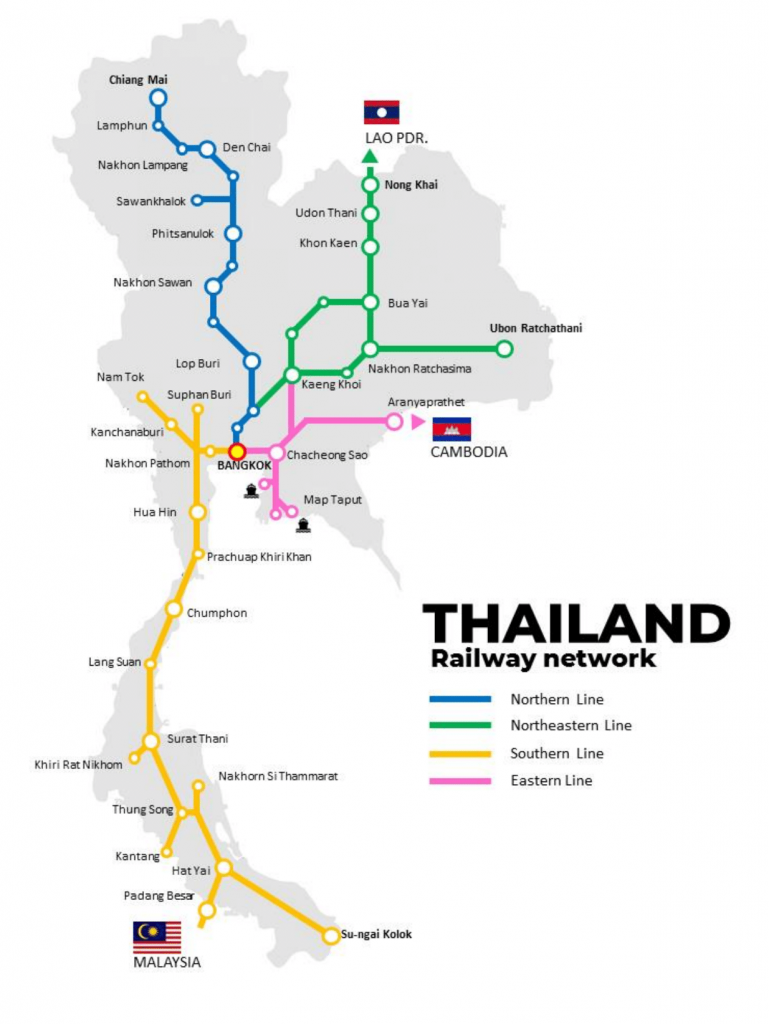
The State Railway of Thailand was founded as the Royal State Railways of Siam (RSR) in 1890. King Chulalongkorn ordered the Department of Railways to be set up under the Department of Public Works and Town and Country Planning. Bangkok – Ayutthaya, the first line was inaugurated on 26 March 1896. The Southern Line, Bangkok Noi (Thonburi) – Phetchaburi was first operated on 19 June 1903.
Unlike the Southern Line, the Northern, Northeastern, and Eastern Lines had been originally built to European standard gauge (1,435 mm.) before they were entirely changed to Meter Gauge(1,000 mm.) in September 1919, taking 10 years for regauging of all lines. On 1 July 1951, RSR changed its name to the present State Railway of Thailand (SRT).
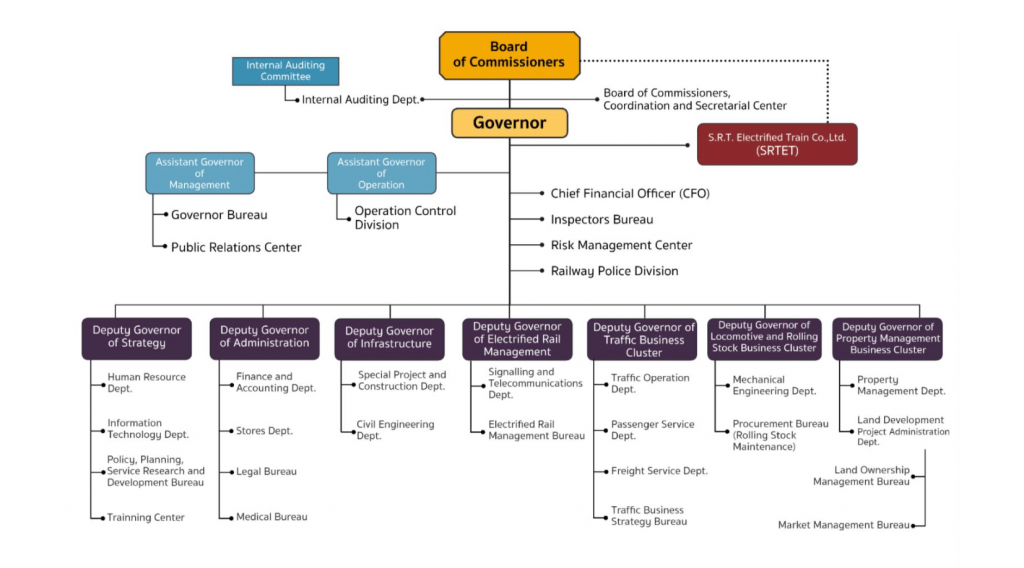
Due to global challenges, the State Railway of Thailand has to develop human resources to support the mass transit and freight transport. The restructured organization is presently issued.
Objectives of the Railway Enterprise Plan 2017-2021
- To enhance the quality of modern rail transport service and good management to promote national competitiveness under changing environment.
- To improve the performance of the Railway Both primary and secondary businesses Including effective cost management.
- To achieve the development of organizations and personnel in line with the rail infrastructure investment plan. This will lead to the long-term competitiveness of the Railway.
- To achieve the integration of cooperation among various departments of the Railway in pushing the railway vision. Efficiency and effectiveness.
- To develop the organization to be integrated and connected To make the operation more efficient.
Vision
To be the best state rail operator in ASEAN in 2027
Mission
Expanded rail service capability And operations to meet the needs of service users both in terms of quality and transportation efficiency
Integrated and comprehensive connectivity across land, water, air, end-to-end.
Create sustainable growth Through proactive business And effective cost management
Promote the spread of prosperity And environmental friendly Through basic transportation services to the country Institutions and Society
Apply digital systems with international standard technology and innovation. To increase operational efficiency and create competitive advantages
Organization Chart
Strategies
The success of a strategic plan is measured by indicators of the strategic level of core business and non-core business, which is measured by the production process and service process. Strategic indicators have goals that make EBIDA positive. The committee that drives the plan will have the duty to monitor and improve. Problems and obstacles for the operation In addition, the Committee should have the power to incur the sanctions tied to the gainsharing principles and allocate the rewards based on the weight, proportion, responsibility of each group or individual. Deputy Governor, the monitoring and improvement of the plan The strategy can be carried out in multiple cycles until the goals of the strategic plan are achieved: increase revenues, reduce positive EBIDA expenses and increase the proportion of rail transport volumes.
Strategy 1
- To increase the capacity of rail transportation service.
- Develop a railway network to connect between regions.
- Increase the number of locomotives and casters in accordance with the business plan.
- Development of signaling system.
- Maintenance optimization of infrastructure to meet the standard.
- Building Confidence in Safety.
Strategy 2
- Increasing income and reducing expenses.
- Increase management efficiency in the core business.
- Developing the area around the big station.
- Study and develop new business.
- Cost reduction.
Strategy 3
- Mobility and improving performance.
- Have a connected information technology system and support decisions to promote performance.
- Organization management and development.
- Human Resource Management and Development
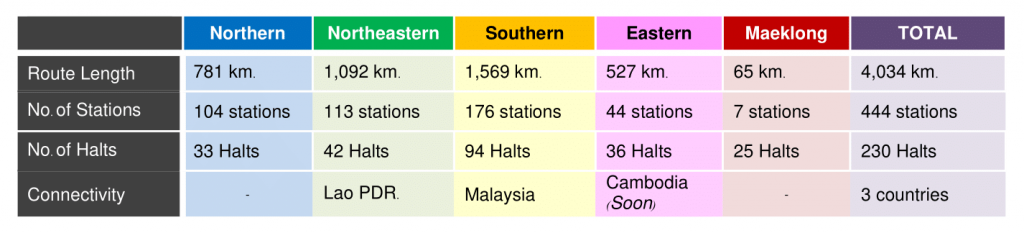
Rail Network